Quick Navigation
Jump to any section of this article
Introduction
Have you ever wondered why most day traders crash and burn? The common consensus online suggest that nearly 95% of day traders fail, a staggering statistic backed by research from various financial analyses (e.g., Barber & Odean, 2000). But why does this happen? In this post, we’ll dive into compelling statistics and behavioral insights to uncover the pitfalls and what you can do to stand out from the crowd.
Study’s done on trading behaviour
Let’s look at some studies done that showcase the pitfalls of trading.
Study 1: Do Day Traders Rationally Learn About Their Ability?
A study by researchers from the University of California and Peking University source reveals that over 75% of day traders quit within two years. Only 15% continue trading after three years, with 56% abandoning the practice after just one year. This high dropout rate underscores the challenges of day trading. For perspective, if 100 students enrolled in a three-year college program, only 15 would graduate, yet this statistic doesn’t indicate whether those 15 would pursue trading as a career.
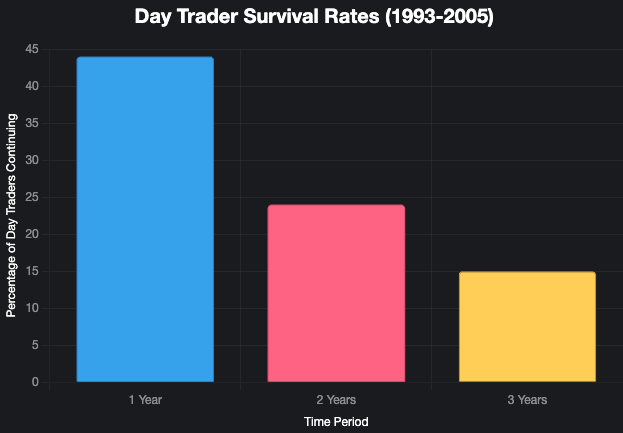 Figure 1: Survival rates of day traders with at least 10 days of experience, showing the percentage still trading after 1, 2, and 3 years (1993-2005).
Figure 1: Survival rates of day traders with at least 10 days of experience, showing the percentage still trading after 1, 2, and 3 years (1993-2005).
The same study concludes that only about 5% of day traders with at least 10 days of experience achieve net positive returns over the long term, with less than 3% consistently profitable. Profitable traders are less likely to quit and tend to maintain or increase their trading activity compared to unprofitable traders, who are more likely to reduce activity or exit. Most day traders fail due to high trading costs (commissions and taxes), persistent losses, overconfidence in their abilities, and non-financial motivations like the thrill of trading or social pressures, which lead many to continue despite poor performance.
Building on the previous statistics, only 15% of day traders persist beyond three years, and of those, only a small fraction are profitable. The majority continue trading despite losses, driven by overconfidence, the thrill of trading, or a failure to recognize their lack of skill.
Study 2: Just How Much Do Individual Investors Lose by Trading?
A 2009 study reveals why individual investors consistently lose money trading, shedding light on the pitfalls. Active trading slashes individual portfolios by 3.8% annually, driven by trading losses (27%), commissions (32%), transaction taxes (34%), and poor market timing (7%). The study pinpoints aggressive orders, impulsive buys at high prices or sells at low prices—as the source of nearly all individual losses.
.png) Figure 2: What amounts to trading losses?
Figure 2: What amounts to trading losses?
Why do traders fail? Many treat trading like gambling, chasing the thrill of quick wins, which fuel excessive, costly trades. The study found that when an alternative gambling option became available, stock market activity dropped by about 25%, suggesting some traders were hooked on the market’s adrenaline rush. Overconfidence is another culprit, with traders overestimating their ability to outsmart the market, leading to reckless, uninformed trades. High trading costs, including commissions and taxes, erode returns, especially for frequent traders.
Individuals hold on to losers longer and sell winners too soon, resulting in worse outcomes. This is the disposition effect. These lessons explain why most traders, like the 15% who persist beyond three years, struggle to achieve the rare profitability seen in just 5% of traders.
Study 3: Do Individual Investors Trade Stocks as Gambling?
A 2015 study from the University of Hong Kong uncovers why some individual investors lose money trading, pointing to a gambling mindset as a key driver. When large lottery jackpots emerge, stock trading by individuals drops by about 7%, and overall activity falls by around 5%, suggesting many treat the market like a casino. This substitution effect is strongest for stocks they favor. Those with high volatility, skewed returns, or recent gains highlighting a chase for thrill over strategy.
Many see trading as a gamble, seeking the rush of quick wins, much like playing the lottery. The study shows trading dips significantly when alternative gambling options appear, implying some investors swap stocks for lotteries when the prize is big enough.
Study 4: In Search of Attention
A 2009 study reveals another layer to trader failures: attention overload. Using Google search data (Search Volume Index or SVI), it shows how retail investors, driven by hype, pile into stocks like IPOs, where searches spike over 40% and first day returns hit only to reverse later. This mirrors gambling, as traders chase excitement rather than strategy. Attention also fuels overconfidence, pushing prices too far and boosting momentum by 2.45% yearly among popular stocks, often leading to losses when trends fade. Even a 1% search increase triggers a 0.02% rise in orders, piling on trading costs.
Recent Insights (2020+)
Recent research adds modern context. A 2023 study found that social comparison on digital platforms drives riskier, more active trading, lowering satisfaction. A 2024 study by a Korean investor analysis showed overconfidence and excessive trading widen profit gaps. A 2020 German study linked economic concern (via FEARS index) to prolonged selling by less sophisticated traders, while a 2022 Bangladesh study highlighted emotional decisions over strategy.
Why It Matters: These trends amplify older findings, showing attention, emotion, and overconfidence still trap 95% of traders today.
What Can be done?
The studies reveal common pitfalls: gambling mentality, cutting winners short, letting losers run, overtrading, and poor risk management—all fueling the 95% failure rate. The good news? These can be overcome with dedication.
I’ve created a free course addressing these exact issues. Learn to ditch the gambling mindset, build a solid trading plan, and treat trading like a business not a thrill ride. Key strategies include:
- Risk Management: Set stop-losses and position sizes.
- Strategy Development: Follow a tested plan, not impulses.
- Education: Continuously learn to counter overconfidence.
Access the course here: https://yungzkittlez.com/courses. Start your journey to join the 5% who thrive!
Found this helpful?
Share this article with your trading community


